The more complex our corporate world becomes, the more crucial it is to be able to adapt to changes. Psychological safety is the key to creating a learning environment that makes people feel safe. But how can you make your business more psychologically safe? The answer is in your own emotional intelligence development.
Knowing thyself – is the heart of emotional intelligence. Self-awareness helps people understand and connect with oneself and others on a deeper level. This article will guide you on how to build a psychologically safe business environment and which EQ skills are required for each step.
What is Psychological Safety and Why Is It Important?


A psychologically safe environment allows employees to voice their opinions, experiment with innovative ideas, try new behaviors, and seek constructive feedback.
According to Harvard Business Review, psychologically safe environments support the development of high-performance teams. These environments also encourage team learning environments across multiple businesses.
While this environment can help create innovative learning environments, it can also carry risks for employees.
For instance, an employee that voices their opinion may challenge the status quo and incite hostility from the group. Also, leaders may see an employee as a failure for trying a new method that didn’t work.
Employees who want to learn new skills at work need a psychologically safe environment where they can try new behaviors without feeling ashamed or being punished if they don’t work as expected.
It takes repeated practice to master a new skill, which is why having a psychologically safe environment is critical. In fact, employees are unlikely to continue practicing a skill if they are shamed or called a failure, which will stunt innovation.
Group norms and leadership style are very important for creating a psychologically safe environment for employees to thrive.
Group Norms for Psychological Safety
Norms are set of rules the group holds for each member. These norms are mostly subconscious, yet they affect whether members feel psychologically safe in profound ways.
The group must abide by these two norms, which will help members feel psychologically safe.
Norm 1: A culture of acceptance
A norm for the group is unconditional acceptance, which allows each member the space to take risks and learn from failures. Suppose a member tries a new approach to sales that didn’t work as planned. Instead of shaming the member, the group offers constructive feedback that can help land the sell the next time.


Since members know they are unconditionally accepted, they engage in constructive confrontation when needed. The group will not oust members that challenge the status quo, which results in creative collaboration.
Acceptance allows the group to build trust and grow together. Members feel safe because they know the group will unconditionally accept them help them succeed.
A culture of acceptance must have members who score high on the EQ skills: Interpersonal Relationships, Empathy, and Social Responsibility.
The EQ skill Interpersonal Relationships suggests that the group can build and keep long-term, healthy relationships with each other. Empathy means understanding and respecting how each group member feels. Lastly, Social Responsibility is about putting the needs of the group above personal needs.
If you need a refresher on the 15 EQ skills, check out my blog!
Norm 2: A culture of open communication
A culture of open communication allows members to notice and respectfully address problems as they happen. Members feel safe voicing their opinions because the group won’t shame them.


Conversely, suppressing communication leads to resentment and could affect the groups’ willingness to collaborate.
Open communication is important for building stronger relationships. Members can console each other and offer strategies during challenging times.
Thus, a culture of communication consists of members who score high on the EQ skills Emotional Self-Awareness, Emotional Expression, Assertiveness, and Empathy.
The EQ skill Emotional Self-Awareness helps members understand why they feel certain emotions. Emotional Expression and Assertiveness helps members communicate what emotions they are feeling and how to get their needs met. While Empathy ensures they consider each others feelings and remain respectful.
Leadership Style for Psychological Safety
Leaders also have an impact on whether or not a psychologically safe environment is possible. Unfortunately, average leaders are unaware of their environment and use the same style in every situation. In other words, they lack Emotional Self-Awareness and Flexibility.
Conversely, emotionally intelligent leaders know that certain situations call for a different leadership styles. In essence, the ability to use different styles separates the emotionally intelligent from the average leaders.
According to Daniel Goleman, there are six different emotionally intelligent leadership styles.
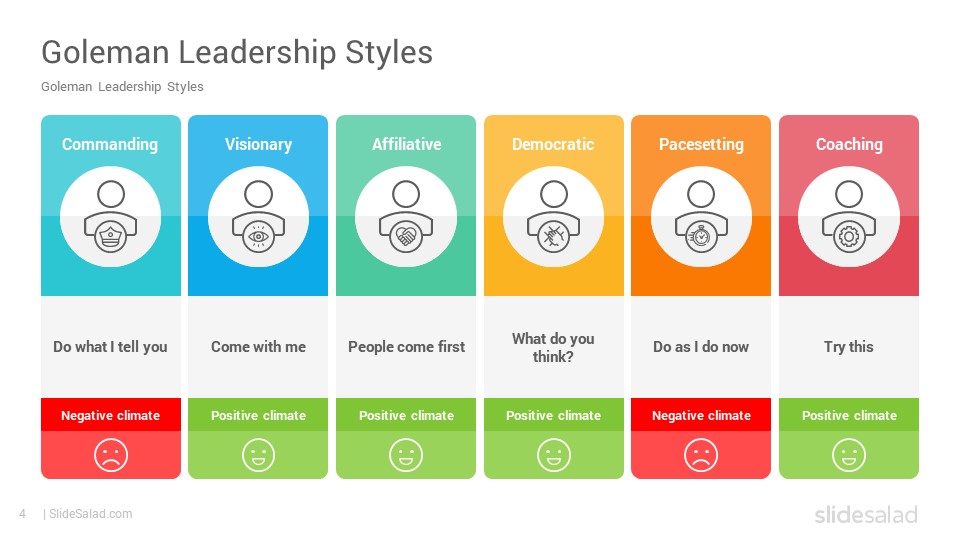

Overall, four out of the six leadership styles foster open and collaborative environments – Coaching, Authoritative, Affiliative, and Democratic.
Four Emotionally Intelligent Leadership Styles
Coaching
The Coaching leader asks thoughtful questions and focuses on employee self-development. Coaching leaders care about their team and work to help them develop their strengths and weakness.
This style works best in helping employees improve their performance or develop long-term goals.
Self-Actualization, Emotional Self-Awareness, Assertiveness, Interpersonal Relationships, Empathy, and Reality Testing are the EQ skills required for the Coaching leadership style.


Authoritative
The Authoritative leader communicates a meaningful vision and inspire the team in reaching their goals. Authoritative leaders know how to motivate employees towards action, and help them figure out what steps they need to take.
This style works best when the vision needs to change or when the team looks to the leader for direction.
Self-Regard, Self-Actualization, Emotional Expression, Interpersonal Relationships, Social Responsibility, and Optimism are the EQ skills that best serve the Authoritative leader.
Affiliative
The Affiliative leader truly cares for their employees and fosters a positive workplace environment. Meaning, this leadership style focuses on building stronger relationships with employees, and prefers harmonious working teams.


This style works best to help mediate conflict among team members and to motivate during uncertainty.
Emotional Self-Awareness, Emotional Expression, Interpersonal Relationships, Empathy, Social Responsibility, and Optimism are the EQ skills required for an Affiliative leader.
Democratic
Lastly, the Democratic leader values employees and wants to hear their thoughts and opinions. This leadership style promotes a collaborative workplace environment.
This style works best when trying to build consensus or get buy-in from the team.
Self-Regard, Emotional Self-Awareness, Emotional Expression, Interpersonal Relationships, Empathy, and Social Responsibility are the EQ skills that comprise a Democratic leader.
Conclusion
An environment that is psychologically safe gives employees the chance to try out new behaviors or skills without fear of being punished or ridiculed.
This environment is important because it encourages employees to take risks and learn from their mistakes, which leads to innovation.
Group norms and leadership style are two components that influence whether employees feel safe in their environment. The group must always be willing to accept each other and communicate openly.
More so, the leadership style should be open and collaborative. Coaching, Authoritative, Affiliative, and Democratic styles are the four leadership styles that cause employees to feel safe.
Employees need a lot of support from their group and leader to feel safe at work. Each employee has unique skills and talents that can contribute to the groups effectiveness.
Employees will authentically express themselves if the environment is supportive and nurturing. We all learn from failures and mistakes. Leaders shouldn’t punish employees for adapting their approach and trying to learn a new skill.
I post new articles every Tuesday and Thursday and update my podcast every Monday, Wednesday, and Friday. Please subscribe to my newsletter if you enjoy my content.
Bianca Cardenas, M.S., Ph.D., is a Fellow in Executive Assessment and Consulting with Leadership Worth Following. Dr. Bianca Cardenas empowers leaders to transcend competition by helping them unlock their people's potential.