It’s nearly impossible to run a business without leaders well-versed in planning, operations, finances, and strategy. These four areas are known as the executive skill suite. Influential leaders focus on the bigger picture while building bridges between departments and uniting people toward the mission. To accomplish this, you must first understand how to drive action towards the vision with proper planning. This article focuses on the first executive skill suite, planning. Business plan components, the three types of planning, and suggestions for implementation are discussed.


What is Business Planning?
A well-thought-out business plan includes long-term strategic goals, the steps to reach those goals, and any projected income and costs. Simply put, business planning has an eye toward the future while looking out for their stakeholders best interest. It’s crucial to have alignment across the business to drive results; thorough business planning ensures proper alignment.
Essentially, there are two main facets to any good business plan. The first is to establish clear goals connected to the vision. Ultimately, this will help everyone understand the business’s hopes to accomplish within a certain time. The second half ensures that everyone is working in the right direction towards achieving the vision.
Keith is the new VP of Operations for a small electronic store, GenX Electronics. One of the first things he noticed was the lack of direction within the company. Keith realized it would be impossible to create alignment throughout the business without proper guidance. He worked with the executive team to create a business plan outlining the following: strategic goals, operations, industry, marketing objectives, and financial projections.

Strategic Goals
These goals are measurable tasks that will help the business work towards the overall vision. While Keith met with the other executives, he ensured they created strategic goals that met four essential criteria. The goals had to have a purpose that could drive action. Linking strategic goals to the vision was a great way to get departments to work together.
Strategic goals also had to look far into the future and be long-term. Keith asked his team, “what would GenX Electronics have to do to leave a mark in the world?” This allows the team to work backwards and identify the needed steps to reach the vision. Lastly, goals had to be actionable and measurable; which helps create action steps that leaders can measure as the team progresses.
Operations
This section outlines the who, what, where, when, and how much to operate your day-to-day business. An operations plan explains the location, equipment, inventory, goals, workflow process, and timelines. In other words, how you got the business off the ground and the ways you deliver your product or service. An operations plan is helpful for investors looking to learn more about how you run your business. From there, they can decide whether the investment is worth the risk.
Industry


The industry section consists of two parts: an industry overview and an explanation of your position within your industry. Before writing this business plan section, it is critical to conduct market research. A great place to start your research is with the Bureau of Labor Statistics, which offers information on different industries within the market.
Once you’ve completed your research, you can start thinking about where you fall within your industry. This includes defining your mission, company history, description of your products and services, target market, competitive advantage, and growth plans. Keith created an industry summary to help investors understand: what they do, whom they serve, their purpose, what sets them apart from the competition, and how they plan to achieve these goals.
Marketing
A marketing plan lays a road map for how your marketing should move your business forward. The results of industry research form the basis of the marketing plan. This helps everyone understand your target customers, what they value, and what they want. Also, this section outlines how you will find new customers, boost sales, achieve goals, and expected returns.
Marketing goals are small, short-term goals that help guide campaigning efforts to reach target customers. These goals are vital because they help members understand their role in marketing’s overall success. Keith ensured that the marketing goals were SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-based) to be as straightforward as possible. For example, one goal was to increase sales revenue by 10 percent at the end of the quarter.
Financial Projections
If you’re looking for more attention from investors, you should focus most of your efforts on this section. Financial projections use financial data showing how much money is coming in and how much will be going out. If you don’t have financial data, one way to show this is through sales forecasting. This method involves breaking down quarterly sales by the units sold, their cost, and how many units you expect to sell. If you already have financial data, a summary of your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement will work instead.
Why Is Business Planning Important?
Business planning acts as a road map for your business and stakeholders. Highly detailed planning gives management a starting point to create and implement action plans that align everyone towards the vision. More so, there’s a much higher chance of success through planning. Businesses that create plans and use them to drive their strategy experience a 30 percent growth rate. Keith’s new business plan help department leaders set realistic sales goals that will ultimately contribute to GenX Electronics’ strategic goals.
Keith noticed a growing market in virtual reality in his industry. So, he decided to work with interested lenders to fund the initial investment. There’s a higher chance of attracting investors who can help GenX Electronics grow with a business plan in place. A plan gives lenders an in-depth breakdown of a businesses growth projections, revenues, and costs. This data helps them decide whether the investment is worth the risk.
Keith worked with other leaders to create a strategic plan outlining GenX Electronics’ strategic goals for each department.

Strategic Planning
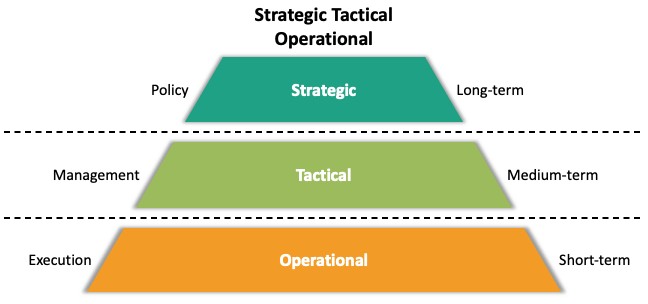
A business can’t run efficiently without a clear direction of where it needs to go. Strategic planning defines a vision for the future and the steps to get there. The goal is to outline strategic priorities, direct needed resources, and improve operations to make sure everyone works towards the vision. An effective strategic plan communicates where the business wants to go, what it needs to do to get there, and whether or not it was successful. Open communication between departments is vital for success because it makes collaboration easier. Once the strategy is in place, two types of planning ensure alignment towards the vision: tactical, and operational.
Tactical Planning
After the strategic plan is put into action, mid-level leaders work on tactical planning; this involves setting specific goals for each division. It is much easier to reach long-term goals if you break them into manageable chunks. If strategic planning is GenX Electronic’s long-term vision, then tactical planning is the way to get there in a certain amount of time.
Sam, the VP of technology, realized that his team could help reach the vision by implementing a technological process. Sam set up a client relationship management (CRM) platform. This system is a very important customer database for GenX Electronics. It keeps track of what electronics customers own, how often they use them, and how much money they spent. As you can see, tactical planning ensures everyone focuses on the same goal: the long-term vision.
Operational Planning
An operational plan ensures that each manager and employee knows what to do and when to do it. This section is highly detailed and outlines the day-to-day tasks that support the tactical plan. Suppose tactical planning is achieving the long-term goals within a certain amount of time. In that case, operational planning is the blueprint for how a department will complete each task contributing to long-term goals.


Since operational planning requires the most level of detail, Sam has to consider certain steps before rolling out the CRM platform project:
Define Goals and Strategy
Once Sam knows how the CRM project fits into the bigger picture, he needs start plotting his strategy. Sam needs to figure out the project’s goals and create a strategy to help him achieve those goals. He realized that he needed to draft a scope of work that outlines the required work and the steps to do it. Sam also needs to identify the stakeholders for this project and make sure they remain in the loop.
Plan Out Activities
Sam must be as specific as possible when planning the activities for a project. He must outline the plans to reach each goal and break them into manageable chunks. The easiest way to figure out the preceding steps is by working backwards, starting with the goal. Sam sets a goal of choosing an affordable CRM platform with an ROI of 20 percent. That means the a required step involves collecting ten quotes from vendors to compare their projected returns.
Assign Roles and Responsibilities
After outlining goals and creating a strategy, Sam needs to assess each team member and assign roles that best suit their skills. He must be as specific as possible while outlining each member’s tasks and deadlines. After making a plan and assigning each member a role, Sam should meet with each member separately to address any questions or concerns. Once everyone understands their role and responsibilities, a reward system can help encourage performance.
Monitor and Adjust
Lastly, Sam must monitor the team’s progress toward implementing the CRM platform and make adjustments when needed. Sam should remain flexible to the needs of his team and work to guide them through the project. Creating work reports is an effective way to assess the teams’ performance throughout the project. Also, the team can have weekly post-project meetings to discuss ways to improve the process and ensure everyone remains up to date.
Conclusion
Leaders must be well-informed in the four executive skill suite areas: planning, operations, finance, and strategy. Business planning is a necessary precursor that ensures the proper goals are in place, which creates alignment toward the vision. A business plan must include: strategic goals, operations, industry, marketing objectives, and financial projections. A thorough business plan will guide members in the right direction and can attract investors. Once a business plan is in place, strategic, tactical, and operational planning guides the achievement of the vision through quarterly goals or day-to-day tasks. Thorough business planning helps leaders understand each department’s interworkings, guiding strategic thinking and effective decision-making.
Bianca Cardenas, M.S., Ph.D., is a Fellow in Executive Assessment and Consulting with Leadership Worth Following. Dr. Bianca Cardenas empowers leaders to transcend competition by helping them unlock their people's potential.







This is a good tip particularly to those
new to the blogosphere. Short but very precise info… Thanks for
sharing this one. A must read post!